CKDTree (1)
Concurrent KDTree with Snapshots, implemented in Java. This article is about some details in implementation.
Basic Idea
The methods used in this structure is heavily based on ideas in CTrie (snapshot) and Non-blocking Binary Search Trees (search, insert and delete).
- RDCSS
- GCAS
- Mark and Flag
- Leaf-oriented tree
Problems and Solutions in Implementation
下面是实现的时候遇到的问题和自己对一些细节的思考,有的已经在两篇论文里面有所记录,但是自己没注意,又踩坑了,还有的是这个结构的设计隐含的问题。
Dummy Nodes
由于Non-blocking Binary Search Trees中的insert操作是需要mark parent的,因此,对于一棵空的tree(有一个root),parent并不存在,insert无法适用于这样的情况。delete也有类似的问题。
为了避免结点数目很少的时候需要考虑很多复杂的情况,Non-blocking Binary Search Trees里提到了使用两个key为\(\infty_1\),\(\infty_2\)(其中\(\infty_1 < \infty_2\))的Dummy nodes,\(\infty_1 < \infty_2\)这样的关系是为了保证Binary Search Trees的性质。
由于Java中,无法使用Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY来得到两个key,使得\(\infty_1 <
\infty_2\),所以就干脆不管他们的关系,root的左右child都使用Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY作为key。
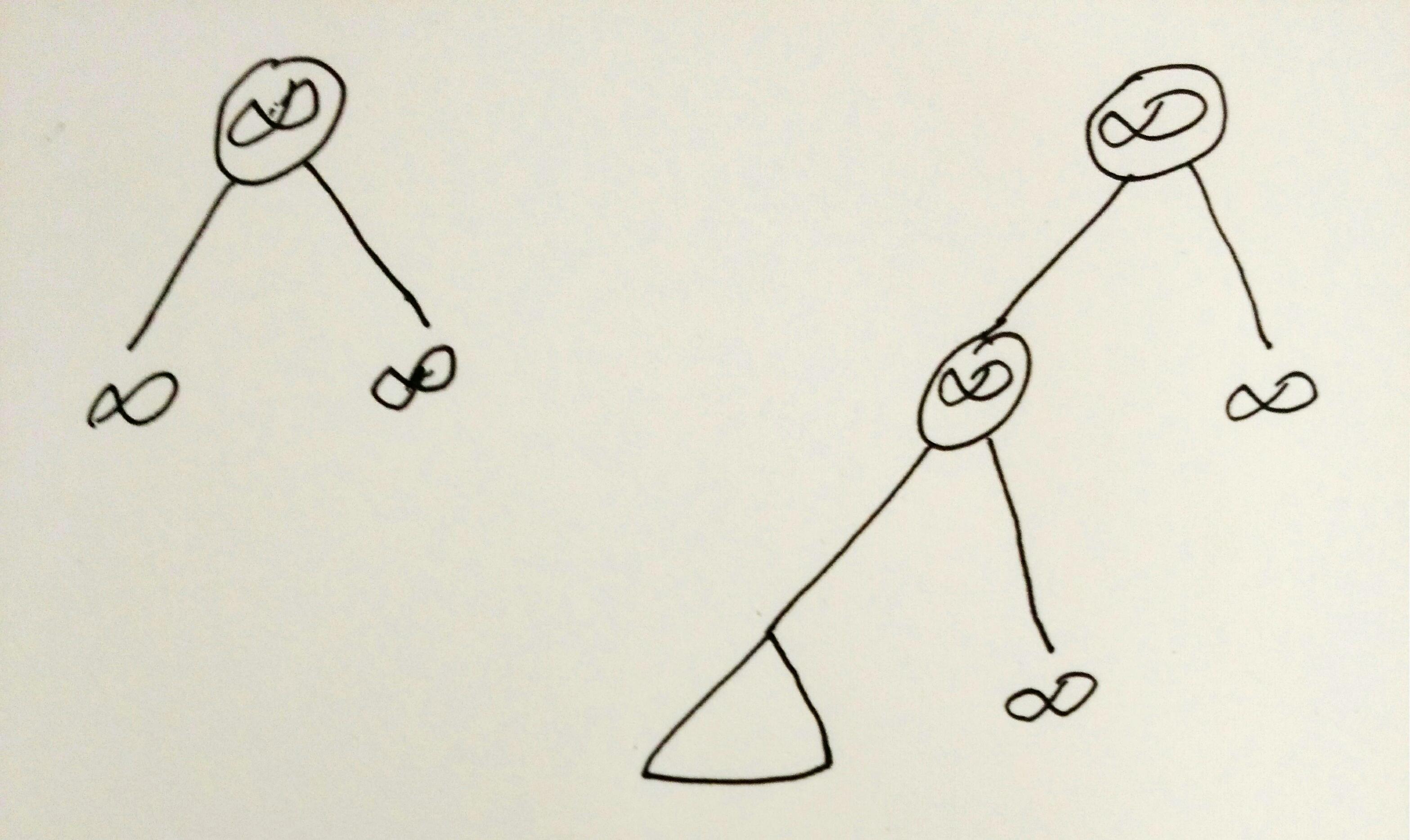
这样一来, 1. 只有在insert第一个key或者delete最后一个key的时候需要操作leaf dummy node。 2. 除(1)以外,所有update都发生在上图三角形的sub tree里面。
Right Child of Root
既然没有key会进入root的right child,那么为什么不把root的right
child设置为null。
不行,这个也是在写后续代码的时候发现的。进行helpMark1和helpMark2的时候,需要判断GCAS处理grand
parent哪边的child,
1 | if (info.p == info.gp.GCAS_READ_LEFT_CHILD(this)) { |
如果要delete的leaf是children of the left child of
root,也就是说此时tree里面只有一个key。存在这么一种可能性,同时有多个thread来进行delete,其中一个thread已经成功进行了delete,其他某些的thread还没有执行上述代码。当开始执行以后,就会发现p不等于gp(即root)的left
child,此时如果root的right为null,那么就会出错。
helpMark1和helpMark2都包含上述操作,只是仅仅helpMark1才会触发问题。
Type Test in
helpMarked1
当要delete的leaf,它的sibling是leaf时,helpMarked1来处理这种的情况。
在single
thread的情况下,helpDelete在判断sibling的类型以后,如果是leaf,那么helpMarked1就会执行。
在multithread的情况下,某个thread看到update信息以后就直接执行helpMarked1,但是此时sibling的类型是不知道的。因为从update信息被发布,到helpMarked1被执行,sibling可能早就被其他thread改变了,如果变为internal
node,
1 | Leaf<V> ns = new Leaf<>(sibling.key, ((Leaf<V>) sibling).value); |
那么上述代码就会报错。
Mark in helpDelete
Non-blocking Binary Search Trees提到marked的结点是不可更改的,实现的时候没有很在意,测试的时候就遇到了麻烦。
helpDelete(1)首先mark parent,(2)read
leaf的sibling,(3)根据sibling的类型来进行后续的操作。
(1)和(2)的顺序是不能改的,这也是mark的意义所在。mark以后,helpMarked1和helpMarked2中还会再次读取sibling,并用于构造新的node,然后GCAS
grand
parent的child。如果不能保证helpDelete中leaf的sibling在后续的操作中不变,那么构造出的新node很可能就是错的。
startGen in
searchKey
这个结构使用了Ctrie里GCAS的idea,在search的时候来update从root到leaf的path。search使用的version number是在开始进行search前从root里read的。为什么不到每个node的时候就read一次version number?
因为如果在search到某个内部的结点的时候,执行了snapshot操作,那么root的version number就变了。此时search中read root的version number,就会造成path的错误更新,上半部分是老的version number,下面有一条新的version number的分支。
Retry after GCAS in
searchKey
searchKey中,如果发现要前往的branch是internal
node,并且version低于startGen,那么就需要创建那个internal
node新版本的copy,然后把cur node的branch设置为那个新版的node。
接下来,首先想到的是在cur
node处重试(即下面代码里的continue;),但是如果continue了,那么gp,gpupdate和depth就会被“提前”更新(cur没有往下走,它们却被更新了),尤其是depth,可能被重复的加上了p的skippedDepth。
1 | while (cur instanceof InternalNode) { |
效率低些,但是更为稳妥的办法就是完全重新开始,return SearchRes.RESTART;。
RDCSS
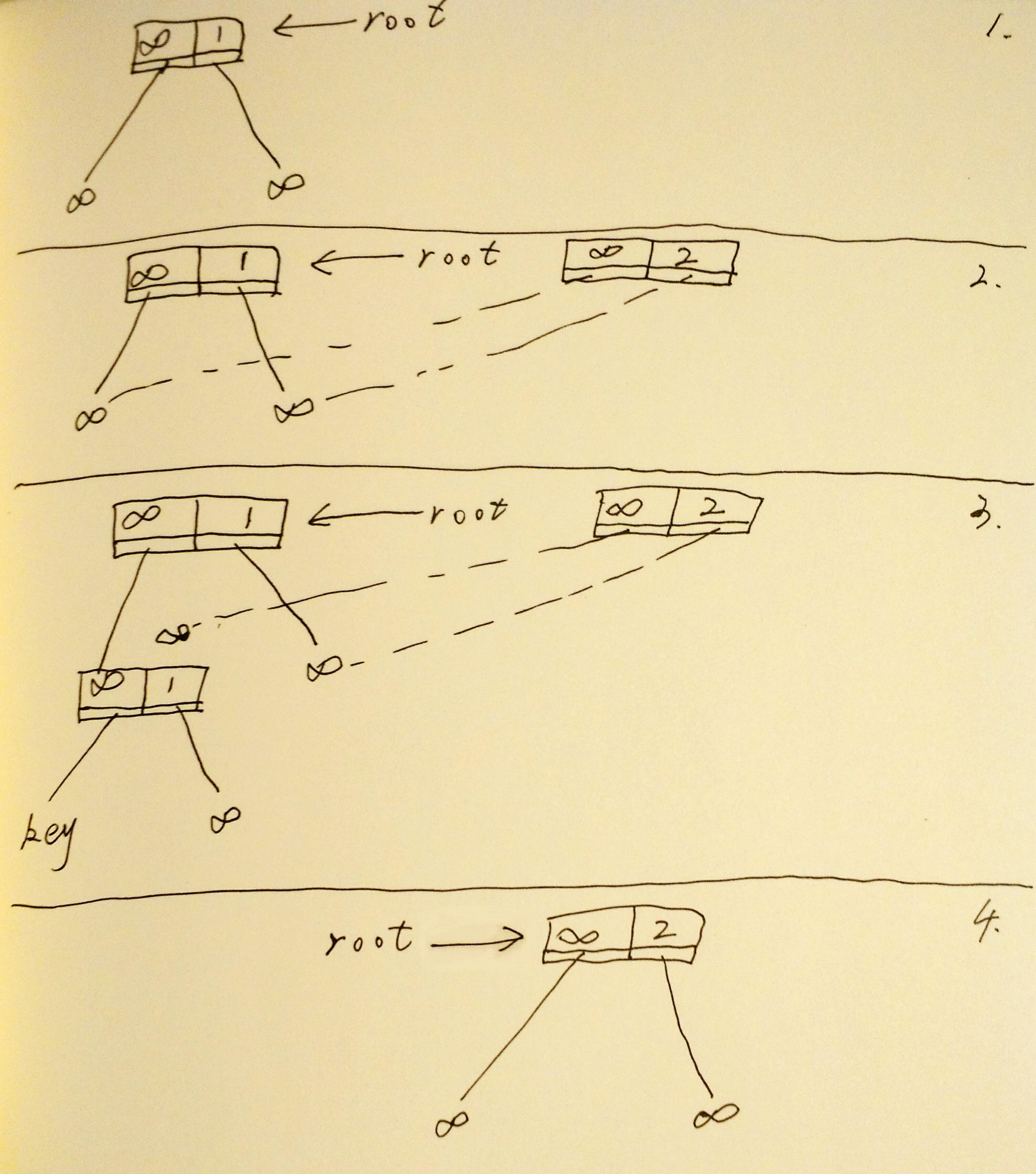
size in Snapshot
未解决。
Readonly Iterator
References
- Concurrent Tries with Efficient Non-Blocking Snapshots, Aleksandar Prokopec, Nathan G. Bronson, Phil Bagwell, Martin Odersky
- Non-blocking Binary Search Trees, Faith Ellen, Panagiota Fatourou, Eric Ruppert, Franck van Breugel
- A Practical Multi-Word Compare-and-Swap Operation, Timothy L. Harris, Keir Fraser, Ian A. Pratt