Thread
Thread
Thread Model
- LinuxThreads
- Default thread implementation since Linux kernel 2.0
- Obsolete
- Next Generation POSIX Thread (NGPT)
- IBM developed version of POSIX thread library
- Abandoned
- Native POSIX Thread Library(NPTL)
- Developed by RedHat
- Better performance and scalability than LinuxThreads
- Since Linux Kernel 2.6, glibc 2.3.5
Memory Layout
- Heap:被所有线程共享。
- Stack:每个线程都有自己独立的 stack。
Thread Stack
| |
Allocate
Implementation
线程栈分配逻辑如下(基于 glibc 2.29.9000),
__pthread_create_2_1创建 thread 时,调用ALLOCATE_STACK宏创建 Thread stack。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10int __pthread_create_2_1 (pthread_t *newthread, const pthread_attr_t *attr, void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg) { // ... struct pthread *pd = NULL; int err = ALLOCATE_STACK (iattr, &pd); int retval = 0; // ... }ALLOCATE_STACK宏调用allcate_stack来执行具体的创建逻辑。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34static int allocate_stack (const struct pthread_attr *attr, struct pthread **pdp, ALLOCATE_STACK_PARMS) { // ... // 从 cache 中查找空闲的栈内存 pd = get_cached_stack (&size, &mem); // 没有空闲的则 mmap 创建 if (pd == NULL) { // ... mem = __mmap (NULL, size, (guardsize == 0) ? prot : PROT_NONE, MAP_PRIVATE | MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_STACK, -1, 0); // ... /* Allocate the DTV for this thread. */ _dl_allocate_tls (TLS_TPADJ (pd)); // ... /* Prepare to modify global data. */ lll_lock (stack_cache_lock, LLL_PRIVATE); /* And add to the list of stacks in use. */ // 将 stack 内存挂到 stack_used list 中 stack_list_add (&pd->list, &stack_used); lll_unlock (stack_cache_lock, LLL_PRIVATE); // ... } // ... // 更新全局栈内存指针 *stack = pd->stackblock; *stacksize = stacktop - *stack; // ... }
Thread-Local Storage
Thread-local storage(TLS)提供了一种机制,使得每个 thread 都拥有一份变量的实例,对 TLS 中变量进行的修改仅对当前 thread 可见。
Common Implementation
- pthread:thread-specific data (TSD)
- ELF(Executable and Linkable Format) TLS
- gcc:
__thread - c11:
_Thread_local - c++11:
thread_local
- gcc:
Example Usages
adext
ThreadData主要用于存储 iconf ctx,确保每个 thread 使用自己的 ctx 来 merge cgi 下发的实验配置。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19static __thread ThreadData* s_td = NULL; class ThreadData { public: ThreadData(); ~ThreadData(); int init(); void reset(); int set_request_info(int bucketid,bs::RankFrontendResp *admergeResult); ::iconf::Context* get_context() { return _ctx; } private: ::iconf::Context* _ctx; };jemalloc 使用 TLS 来保存每个线程特有的数据,避免锁竞争。
1 2 3 4 5#define malloc_tsd_data(a_attr, a_name, a_type, a_initializer) \ a_attr __thread a_type JEMALLOC_TLS_MODEL \ a_name##tsd_tls = a_initializer; \ a_attr pthread_key_t a_name##tsd_tsd; \ a_attr bool a_name##tsd_booted = false;POSIX
errnoerrno is thread-local; setting it in one thread does not affect its value in any other thread.
Implementation
pthread:thread-specific data (TSD)
Example
| |
Memory Layout
| |
Implementation
- 全局分配唯一 key
- 各个 thread 存储自己的 key-value map
以下分析基于 glibc 2.29.9000。
如何访问 Thread Stack
TSD 是存储在各个线程的内存中,要访问 TSD,就需要一种方法来访问线程栈。
glibc 通过调用
clone实现创建线程。如果提供了CLONE_SETTLS,那么会将tls存入 fs 寄存器。1 2int clone(int (*fn)(void *), void *stack, int flags, void *arg, ... /* pid_t *parent_tid, void *tls, pid_t *child_tid */ );在调用
clone时,tls是struct pthread的地址。从而可以通过 fs 寄存器来访问到线程栈。1 2 3 4TLS_DEFINE_INIT_TP (tp, pd); if (__glibc_unlikely (ARCH_CLONE (&start_thread, STACK_VARIABLES_ARGS, clone_flags, pd, &pd->tid, tp, &pd->tid) == -1))glibc,以及各种 TLS 实现中对线程栈的访问都是利用 fs 实现的。
fs 寄存器可以通过如下方式获得:
arch_prctl1arch_prctl(ARCH_GET_FS, &pthread_addr);asm %fs
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8# define THREAD_SELF \ ({ struct pthread *__self; \ asm ("mov %%fs:%c1,%0" : "=r" (__self) \ : "i" (offsetof (struct pthread, header.self))); \ __self;}) struct pthread *self; self = THREAD_SELF;
Create
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17#define PTHREAD_KEYS_MAX 1024 typedef unsigned int pthread_key_t; /* Thread-local data handling. */ struct pthread_key_struct { /* Sequence numbers. Even numbers indicated vacant entries. Note that zero is even. We use uintptr_t to not require padding on 32- and 64-bit machines. On 64-bit machines it helps to avoid wrapping, too. */ uintptr_t seq; /* Destructor for the data. */ void (*destr) (void *); }; struct pthread_key_struct __pthread_keys[PTHREAD_KEYS_MAX]在主线程中调用
pthread_key_create完成 key 的创建。glibc 定义了全局数组__pthread_keys来管理 key,每个进程最多创建 1024 个 key。数组中每个元素的:
seq用于判断 key 是否被使用,为奇数则被使用destr用于存储释放资源的函数指针
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18#define KEY_UNUSED(p) (((p) & 1) == 0) int __pthread_key_create (pthread_key_t *key, void (*destr) (void *)) { /* Find a slot in __pthread_keys which is unused. */ for (size_t cnt = 0; cnt < PTHREAD_KEYS_MAX; ++cnt) { // ... /* Remember the destructor. */ __pthread_keys[cnt].destr = destr; /* Return the key to the caller. */ *key = cnt; /* The call succeeded. */ return 0; } // ... }Set
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18#define PTHREAD_KEY_2NDLEVEL_SIZE 32 // 32 #define PTHREAD_KEY_1STLEVEL_SIZE \ ((PTHREAD_KEYS_MAX + PTHREAD_KEY_2NDLEVEL_SIZE - 1) \ / PTHREAD_KEY_2NDLEVEL_SIZE) struct pthread_key_data { /* Sequence number. We use uintptr_t to not require padding on 32- and 64-bit machines. On 64-bit machines it helps to avoid wrapping, too. */ uintptr_t seq; /* Data pointer. */ void *data; } specific_1stblock[PTHREAD_KEY_2NDLEVEL_SIZE]; /* Two-level array for the thread-specific data. */ struct pthread_key_data *specific[PTHREAD_KEY_1STLEVEL_SIZE];各个线程将 key-value 存储到线程栈中,
- 如果 key < 32,到存储到
specific_1stblock - 如果 32 <= key < 1024,存储到二维数组
specific
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36int __pthread_setspecific (pthread_key_t key, const void *value) { // ... struct pthread *self; self = THREAD_SELF; /* Special case access to the first 2nd-level block. This is the usual case. */ if (__glibc_likely (key < PTHREAD_KEY_2NDLEVEL_SIZE)) { // ... level2 = &self->specific_1stblock[key]; // ... } else { // ... idx1st = key / PTHREAD_KEY_2NDLEVEL_SIZE; idx2nd = key % PTHREAD_KEY_2NDLEVEL_SIZE; // ... /* This is the second level array. Allocate it if necessary. */ level2 = THREAD_GETMEM_NC (self, specific, idx1st); if (level2 == NULL) { // 分配 specific 二维数组 // ... } /* Pointer to the right array element. */ level2 = &level2[idx2nd]; } /* Store the data and the sequence number so that we can recognize stale data. */ level2->seq = seq; level2->data = (void *) value; return 0; }- 如果 key < 32,到存储到
Get
根据 key 的取值范围,决定访问
specific_1stblock,还是specific。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19void * __pthread_getspecific (pthread_key_t key) { // ... if (__glibc_likely (key < PTHREAD_KEY_2NDLEVEL_SIZE)) data = &THREAD_SELF->specific_1stblock[key]; else { // ... unsigned int idx1st = key / PTHREAD_KEY_2NDLEVEL_SIZE; unsigned int idx2nd = key % PTHREAD_KEY_2NDLEVEL_SIZE; // ... data = &level2[idx2nd]; } void *result = data->data; // ... return result; }Delete
pthread_key_delete会把 seq++,置为偶数,表示 key 为被使用,并不会真正的调用destr来进行资源的释放。当线程执行完毕时,
__nptl_deallocate_tsd调用每个 key 的destr执行清理。
ELF TLS
pthread TSD 全局分配 key,需要调用 glibc API 在运行时完成 TSD 的构造和使用,比较复杂,影响效率。因此就有了 ELF TLS。
ELF TLS 是编译器(gcc/clang)的扩展特性,其实现需要如下方面的支持:
- ELF 文件需要区分普通静态全局变量和 TLS 变量
- 程序启动时,动态链接器需要初始化 TLS 变量的段
- 线程运行时,需要为 TLS 分配专门的内存区域,以及动态计算 TLS 的地址
ELF TLS Section
普通 static 全局变量,根据是否初始化分别存储在 .data (已初始化)和 .bss (未初始化,初始化为 0),类似的 TLS 变量存储在 .tdata 和 .tbss 段。
由于 TLS 是各个线程私有的数据,因此线程是不能直接访问 .tdata 和 .tbss 段的。
运行时分配 TLS
Memory Layout
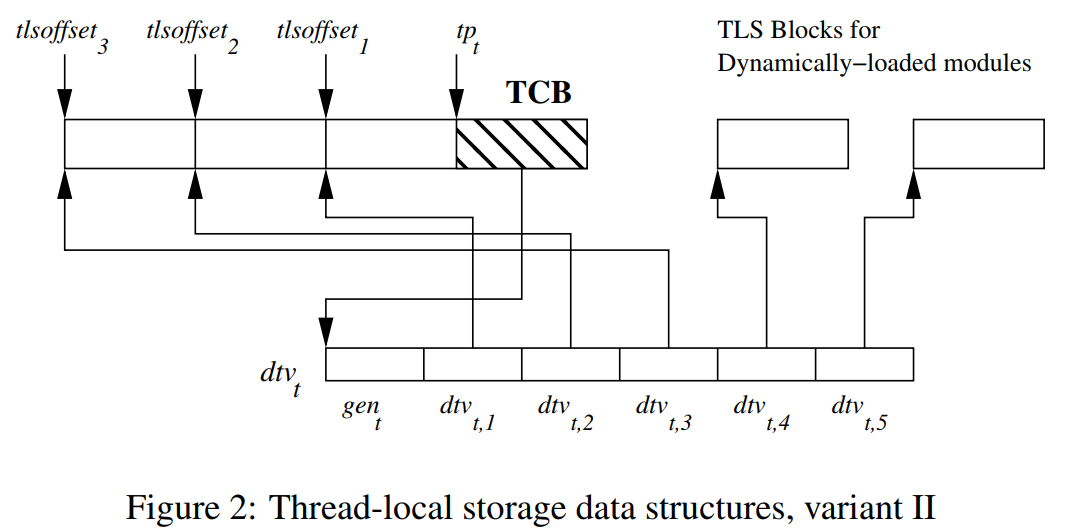
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33low ┌──────┬──────────┐ │ │... │ ─┐ ─┐ │ ├──────────┤ │ │ │header│dtv │ │ │ │ ├──────────┤ │ │ │ │... │ │ │ ├──────┴──────────┤ ├─►pthread struct │ │list │ │ │ ├─────────────────┤ │ │ │tid │ │ │ ├─────────────────┤ │ ├─►thread 1 │... │ │ │ ├─────────────────┤ │ │ │... │ ─┘ │ ├─────────────────┤ │ │ │ │ │stack │ │ │ │ ─┘ ├─────────────────┤ │ │ ───►stack guard(4k) ├─────────────────┤ │header │ ─┐ ├─────────────────┤ │ │list │ │ ├─────────────────┤ │ │tid │ │ ├─────────────────┤ │ │... │ │ ├─────────────────┤ ├─►thread 2 │ │ │ │stack │ │ │ │ ─┘ high └─────────────────┘TLS 的内存布局用两种,对于 x86-64 是如下布局,

tp(thread pointer,也是前面提到的 fs 寄存器的值) 指向 TCB,也就是 pthread struct,TCB 包含了一个 dtv(dynamic thread vector)指针,指向线程的 dtv 数组。
dtv 存储了 TLS block 地址,通过 module ID 和 TLS 变量的偏移量来实现 TLS 变量的寻址。对于 exec,module ID 是 1;动态库(
dlopen)的 module ID 直到加载的时候才会分配。根据 TLS 变量在何处被定义,其存储分为,
- 来自 exec、以及 shared object:
main函数之前加载的 TLS 变量存储在 TCB 前面的 TLS block。dtv[1] 指向这个 TLS block。 dlopen加载的 shared object:TLS 变量在 TLS Blocks for Dynamically-Loaded Modules。
- 来自 exec、以及 shared object:
Allocate
程序启动时,动态链接器将 exec、shared object 映射到进程地址空间,并进行相关初始化,
- 可能会对这两个段进行重定位,并把重定位后的段保存为 TLS 初始化镜像,之后便不再改动
- 调用
_dl_determine_tlsoffset获得每个 module 中 TLS 变量的 offset(在编译的时候决定),offset 表示变量在 TLS block 中的偏移量 - 调用
_dl_allocate_tls_storage分配 TLS 和 dtv 的内存 - 调用
_dl_allocate_tls_init完成 TLS 和 dtv 的初始化
Implementation
- 前面提到线程启动时,
ALLOCATE_STACK宏调用allcate_stack来执行创建线程栈的逻辑,其中调用_dl_allocate_tls是进行 TLS 和 dtv 的分配以及初始化。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9static int allocate_stack (const struct pthread_attr *attr, struct pthread **pdp, ALLOCATE_STACK_PARMS) { // ... /* Allocate the DTV for this thread. */ _dl_allocate_tls (TLS_TPADJ (pd)); // ... }_dl_allocate_tls_init将每个 module 的 TLS 初始化镜像复制到 TLS block。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23void * _dl_allocate_tls_init (void *result) { // ... while (1) { // ... dtv[map->l_tls_modid].pointer.val = TLS_DTV_UNALLOCATED; dtv[map->l_tls_modid].pointer.to_free = NULL; // ... dest = (char *) result - map->l_tls_offset; // ... /* Set up the DTV entry. The simplified __tls_get_addr that some platforms use in static programs requires it. */ dtv[map->l_tls_modid].pointer.val = dest; /* Copy the initialization image and clear the BSS part. */ memset (__mempcpy (dest, map->l_tls_initimage, map->l_tls_initimage_size), '\0', map->l_tls_blocksize - map->l_tls_initimage_size); } // ... }- 前面提到线程启动时,
Example
| |
TLS Access Models
根据 TLS 变量定义的位置,以及访问的位置不同,有以下 4 中使用 TLS 变量的模型。具体采用哪种模式由编译器和链接器共同决定。
General Dynamic
最通用的访问模型,任何地方定义的 TLS 变量,在任何地方访问,都可以使用这个方式。其他模型都是加上各种限制条件以后的优化。
可以用这个公式来表示
dtv[ti_module].pointer + ti_offset。实际可以使用__tls_get_addr来获取 TLS 变量地址。1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15void * __tls_get_addr (GET_ADDR_ARGS) { dtv_t *dtv = THREAD_DTV (); if (__glibc_unlikely (dtv[0].counter != GL(dl_tls_generation))) return update_get_addr (GET_ADDR_PARAM); void *p = dtv[GET_ADDR_MODULE].pointer.val; if (__glibc_unlikely (p == TLS_DTV_UNALLOCATED)) return tls_get_addr_tail (GET_ADDR_PARAM, dtv, NULL); return (char *) p + GET_ADDR_OFFSET; }Local Dynamic
Local Dynamic 是对 General Dynamic 的优化。如果 TLS 变量在同一个模块被定义和使用,则可以使用这个模型。
TLS 变量的 offset 在编译时可以确定,因此可以减少
__tls_get_addr的调用。Initial Exec
如果可以 TLS 变量在程序启动时就已分配好,则采用此模型。
Local Exec
对 Local Dynamic 的优化,如果 TLS 变量在 exec 中定义,在 exec 中访问,则使用这个模型。
通过 fs 寄存器 + 偏移量访问。这种是最简单,也是最高效的方式,和访问局部变量没有区别。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10var_1 = 1; 401194: 64 c7 04 25 fc ff ff movl $0x1,%fs:0xfffffffffffffffc 40119b: ff 01 00 00 00 4011a0: 64 48 8b 0c 25 00 00 mov %fs:0x0,%rcx 4011a7: 00 00 4011a9: 48 8d 91 fc ff ff ff lea -0x4(%rcx),%rdx var_2 = 2; 4011b0: 64 c7 04 25 f8 ff ff movl $0x2,%fs:0xfffffffffffffff8 4011b7: ff 02 00 00 00 4011bc: 48 8d 89 f8 ff ff ff lea -0x8(%rcx),%rcx
gcc: __thread
pass
c11: _Thread_local
同 gcc __thread
c++11: thread_local
相对于 __thread , thread_local 可以在首次使用时自动初始化,线程结束时自动析构。
Summary
- pthread:thread-specific data (TSD)
- 全局分配 key
- 线程栈中的 pthread struct 存储自己线程的 key-value
- 每个进程的 TSD 个数有限,
PTHREAD_KEYS_MAX个 - 需要调用 glibc API 完成 TSD 的构造和使用,逻辑复杂
- ELF TLS
- 效率比 TSD 高
- 使用方便
References
Thread
- Understanding the Memory Layout of Linux Executables
- Understanding Linux /proc/id/maps
- Glibc 线程资源分配与释放–—线程栈
- 虚拟内存[02] Linux 中的各种栈:进程栈 线程栈 内核栈 中断栈
- Threads
- source code of userspace/glibc/nptl/